DABAR (Digital Academic Archives and Repositories) is the key component of the Croatian e-infrastructure’s data layer. It provides technological solutions that facilitate maintenance of higher education and science institutions' digital assets, i.e., various digital objects produced by the institutions and their employees.
DABAR also facilitates establishment and maintenance of a large number of reliable and interoperable institutional and thematic digital repositories and archives, without any costs to the institutions, i.e., DABAR users. By establishing a repository within DABAR, an institution is provided with a reliable, flexible and ready-to-use environment that can be used to collect, store and disseminate various digital objects, as well as maintain those digital collections.
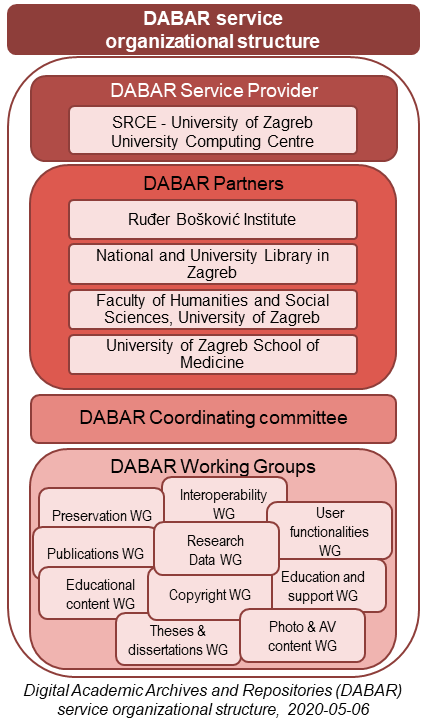
DABAR is a product of collaboration among a large number of institutions and individuals from the academic community. During the further development of DABAR, SRCE relies on the cooperation and support from institutions and individuals from science and higher education community.
DABAR users (institutions) are provided with:
- an institutional repository, under the institution's web domain, which serves as a central place for storing research data, as well as intellectual and creative property of an institution
- total control over access rights and repository content usage
- a possibility of open access publishing and increasing the visibility of the content and the institution itself
- a reliable long-term data storage
- a solution for storing theses and doctoral dissertations described by metadata descriptions prescribed by the National and University Library in Zagreb in accordance with the Act on Scientific Activity and Higher Education
- a possibility to modify the design and content of the repository interface using Drupal content management system
- AAI@EduHr account log-in
- a possibility to establish a thematic repository for the research community.
What can be stored in a repository within the DABAR system?
All digital objects created while conducting scientific research, as well as intellectual and creative property owned by the institution archiving the content. Examples of object types are preprint papers, reviewed articles, conference papers, research data, dissertations, theses, books, teaching materials, images, video and audio files, presentations, digitalized materials… To ensure that objects are searchable, every object has to be described using a prescribed set of metadata during upload.
...and what cannot?
DABAR cannot be used as a back-up system nor a long-distance data storage. Individuals cannot become repository owners, only institutions (one or several) can be owners of a repository within the DABAR system.
What is the DABAR team in charge of?
- providing, connecting and maintaining all the necessary computer resources and storage capacities you might need
- ensuring the safety, stability and high availability of the digital repositories system by using advanced IT technology, making back-up copies, regularly updating system support and continuously surveilling the system
- ensuring data collection from existing information systems to facilitate object upload (e.g. theses’ metadata are taken from the Information System of Higher Education Institutions – ISVU)
- maintaining and developing the application’s functionality by following national standards and global trends in the area of digital repositories
- defining and implementing support for storing and describing digital objects according to the needs of academic and research community
- implementing and promoting standard data exchange protocols (OAI-PMH)
- giving support and educating users, as well as promoting information exchange.
Organizational structure